
The public Java Documentation for Spring Web Flow, a framework for modeling and executing user interface flow.
|
|||||||||
| PREV NEXT | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||

The public Java Documentation for Spring Web Flow, a framework for modeling and executing user interface flow.
See:
Description
| Packages | |
|---|---|
| org.springframework.webflow.action | Common action implementations invokable by flow definitions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.action.portlet | Action implementations that define logic specific to flows executing in a JSR-168 Portlet environment. |
| org.springframework.webflow.config | High-level flow system configuration support within a Spring environment. |
| org.springframework.webflow.context | The external context subsystem for accessing the environment of a client that has called into Spring Web Flow. |
| org.springframework.webflow.context.portlet | The representation of a client request into Spring Web Flow from a JSR-168 Portlet environment. |
| org.springframework.webflow.context.servlet | The representation of a client request into Spring Web Flow from an HTTP Servlet environment. |
| org.springframework.webflow.conversation | The conversation subsystem for beginning and ending conversations that manage the state of user interactions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.conversation.impl | Conversation manager implementations. |
| org.springframework.webflow.core | Foundational, generic types usable by all other packages. |
| org.springframework.webflow.core.collection | Core element collection types used within Spring Web Flow. |
| org.springframework.webflow.definition | Core, stable abstractions for representing flow definitions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.definition.registry | The flow definition registry subsystem for managing containers of flow definitions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.engine | The implementation of the core flow definition artifacts that serve the basis of the flow execution engine. |
| org.springframework.webflow.engine.builder | The flow builder subsystem for building and assembling executable flow definitions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.engine.builder.xml | The XML-based flow builder implementation. |
| org.springframework.webflow.engine.impl | The implementation of Spring Web Flow's flow execution machine. |
| org.springframework.webflow.engine.support | Support implementations for internal engine-specific types. |
| org.springframework.webflow.execution | Core, stable abstractions for representing runtime executions of flow definitions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.execution.factory | Supporting types often used by flow execution factory implementations. |
| org.springframework.webflow.execution.repository | The flow execution repository subsystem for saving, and restoring managed flow executions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.execution.repository.continuation | Implementation of continuation-based flow execution repositories. |
| org.springframework.webflow.execution.repository.support | General purpose implementation assistance for flow execution repositories. |
| org.springframework.webflow.execution.support | Useful generic support implementations of core flow execution types. |
| org.springframework.webflow.executor | High-level executors for driving the execution of flow definitions. |
| org.springframework.webflow.executor.jsf | The integration layer between Spring Web Flow and Java Server Faces (JSF). |
| org.springframework.webflow.executor.mvc | The integration layer between Spring Web Flow the Spring (Portlet) MVC framework. |
| org.springframework.webflow.executor.struts | The integration layer between Spring Web Flow and Struts 1.x. |
| org.springframework.webflow.executor.support | Flow executor implementation support; includes helpers for driving the execution of flows. |
| org.springframework.webflow.test | Support for testing flows and their associated artifacts. |
| org.springframework.webflow.test.execution | Support for testing the execution of a flow definition. |
| org.springframework.webflow.util | General purpose utility classes used internally by the Spring Web Flow system. |

The public Java Documentation for Spring Web Flow, a framework for modeling and executing user interface flow.
Spring Web Flow's packages are partitioned across a set of logical layers. Higher layers depend on the layers directly beneath. Lower layers never depend on higher layers.
The layers of Spring Web Flow, from lowest to highest, are shown below:
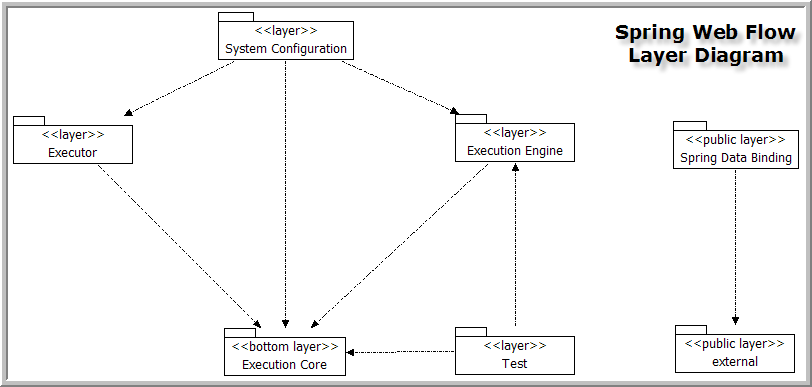
Layer architecture diagram
The description, subsystems, and source packages of each layer are summarized below:
Contains the central public Spring Web Flow API elements. This includes elements to model flow definitions as well as execute those flow definitions. As the "bottom layer", this layer defines key domain interfaces and is highly stable.
Core
Flow Definition
Flow Definition Registry
External Context
Conversation
Flow Execution
Flow Execution Repository
Action
Util
Contains services called "flow executors" that drive the execution of flow definitions. This layer defines the core FlowExecutor service interface and implementation, as well as adaption code for executing flows in several specific environments. Support for Spring MVC, Struts, and Java Server Faces (JSF) environments is housed here. This layer depends on the stable Execution Core, but is not coupled to the more volatile Execution Engine implementation.
Contains concrete implementations of the stable Execution Engine abstractions. This layer defines the finite-state machine that carries out runtime flow execution. It also contains a builder subsystem for assembling flows from externalized resources such as XML files.
Contains support code for testing flow executions. Two types of support are provided: stubs for unit testing engine artifacts, and base classes for writing flow execution integration tests. This layer depends on the Execution Core and Execution Engine layers.
Contains support for configuring the flow executor engine using Spring. A Spring 2.0 config schema is provided. This is the top layer and depends on the Execution Core, Executor, and Execution Engine layers.
|
|||||||||
| PREV NEXT | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||